Graphic design for architecture emerged as a vital approach to complement the intricate lines and forms of buildings, breathing creativity and clarity into the urban landscape. Initially, graphic design served merely as a supportive role in architecture, yet today, it's a thriving discipline with countless possibilities. Whether through branding, wayfinding, or environmental graphics, it enhances spatial comprehension and enriches the visual narrative of structures. While it might initially appear technical and complex, graphic design for architecture is incredibly versatile and engaging--and it's currently experiencing a dynamic evolution. Elevate your architectural projects with the following graphic design strategies and craft a cohesive visual experience.
Architectural renderings
Architectural renderings are pivotal in the realm of graphic design for architecture, acting as a bridge between abstract concepts and tangible visualizations. These renderings incorporate an array of design elements including light, shadow, color, and texture to create lifelike images that convey the intended aesthetic and functional aspects of architectural projects. High fidelity 3D models merge with advanced rendering software to produce imagery that not only captures the spatial essence of a design but also encapsulates the emotional ambiance the structure aims to evoke. The precision in detail helps architects communicate complex design ideas effortlessly, allowing stakeholders to virtually experience spaces that are yet to be constructed, thus playing a crucial role in project approval and development processes.
Floor plan graphics
Floor plan graphics in architecture serve as a crucial component of visual communication, utilizing a combination of geometry, color, and line styles to effectively represent spatial arrangements and design intentions. Precision in the use of line weights and hatching techniques is essential to distinguish different types of walls, partitions, and door placements, ensuring clarity in understanding how spaces interact within a building's layout. The application of color can be strategically employed to highlight important features, such as circulation paths, zoning, or areas of different functions; it enhances visual hierarchy and guides the viewer's attention through the plan. Incorporating symbols and icons for furniture, fixtures, and fittings allows for a holistic interpretation of the spatial environment, offering insight into the intended use and functionality of designated areas.
Elevation illustrations
Elevation illustrations in architecture represent a two-dimensional portrayal of a building's external facade, offering a meticulous depiction that showcases structure, texture, materials, and stylistic elements. These illustrations serve a critical purpose in providing a comprehensive view of the building's design, aiding architects and clients alike in visualizing the final product with precision. Detailed graphical representations include annotations, scale, and measurements, allowing for accurate planning and construction execution. The integration of digital tools enhances the depth of these illustrations by incorporating realistic shading, color palettes, and environmental context, thereby transforming basic sketches into dynamic, immersive visual narratives that thoroughly communicate the architectural vision.
Site layout designs
Site layout design in architecture necessitates a thorough understanding of spatial organization as well as the landscape's interaction with built environments. Designers utilize topographical maps, zoning requirements, and environmental impact assessments to ensure that the placement of buildings, pathways, and green spaces optimally exploits the site's natural features and orientation. Subtle nuances, such as circulation patterns and solar exposure, must be intricately mapped out to maximize functionality and energy efficiency within the layout. Additionally, integrating technology for visualization, such as 3D modeling and digital simulations, plays a pivotal role in planning, allowing architects to predict the performance of landscape elements and their influence on the overall ambience and usability of the development.
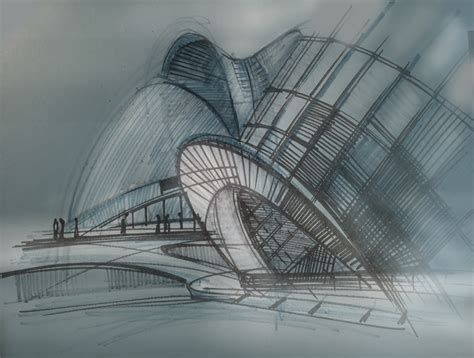
Perspective drawings
In the realm of architecture, graphic design plays a crucial role in the creation of perspective drawings, providing a spatial understanding of proposed projects by capturing the interplay of light, shadow, and form. Architects utilize one-point, two-point, and three-point perspectives to convey depth and dimension, allowing stakeholders to visualize environments in relation to human scale, which is essential for immersive client presentations or public exhibitions. Digital tools, such as CAD software and 3D modeling programs, enhance these drawings by offering precision and realism, incorporating textures and vivid colors that bring blueprints to life. Perspective drawings serve not only as artistic representations but also as analytical documents, demonstrating the impact of design on its surroundings, considering factors like sightlines and vistas, crucial for both aesthetic appeal and functional harmony within urban landscapes.
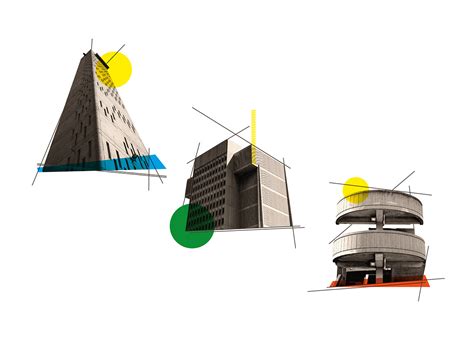
Conceptual sketches
Graphic design for architecture, with an emphasis on conceptual sketches, serves as a pivotal tool in the initial stages of design development, offering a raw, expressive form through which architects can experiment with spatial ideas and communicate abstract concepts. These sketches, often executed with loose, gestural strokes, embody the designer's mental navigation between form, function, and spatial dynamics, highlighting the interplay of light, volume, and texture. They enable a fluid exploration of architectural intent, where the essence of a structure can be distilled into simple lines and shapes, allowing for rapid iteration and the evolution of ideas without the constraints of finalized detail work or digital precision. As such, conceptual sketches provide a visual language that bridges the visionary aspect of architectural thinking with the eventual tangible reality, serving both as a blueprint for more refined designs and a medium for dialogue between architects, collaborators, and stakeholders.
Landscape architecture graphics
In landscape architecture graphics, the integration of natural and built environments is meticulously illustrated, capturing the delicate interplay between vegetation, water features, hardscapes, and the architecture itself. Designers employ a range of tools and techniques, from hand-drawn sketches that offer a raw, organic feel to sophisticated digital renderings that utilize software like AutoCAD or SketchUp, vividly incorporating three-dimensional elements and textures to create immersive visualizations. Photorealistic renderings are complemented by thematic and topographic mapping, which layer information such as plant species, growth patterns, and seasonal changes, allowing for a multifaceted understanding of the landscape's dynamics. The graphics are not mere representations, but strategic planning tools, reflecting sustainable practices by mapping out ecological systems and green infrastructure, thereby demonstrating how well-thought-out design can enhance aesthetic appeal while fostering environmental stewardship.
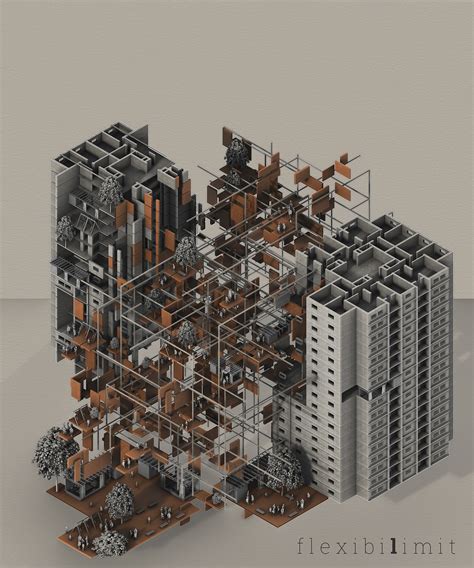
3D modeling for architecture
Graphic design in architecture, particularly through 3D modeling, serves as a pivotal tool in transforming conceptual sketches into tangible visualizations, facilitating an immersive understanding of spatial design. Architects utilize complex software to create detailed models that encapsulate everything from the structural framework to aesthetic finishings, allowing for an exploration of materials, textures, and lighting which fundamentally enhances the presentation and clarity of a proposed architectural project. This process not only aids architects in refining their designs by quickly iterating and testing different scenarios, but it also plays a crucial role in client presentations by providing a realistic interpretation of the final product, thereby bridging the gap between imagination and reality. Furthermore, 3D modeling contributes to improved accuracy in construction documentation, reducing errors and inconsistencies while enabling collaboration across multiple disciplines involved in the execution of architectural plans.
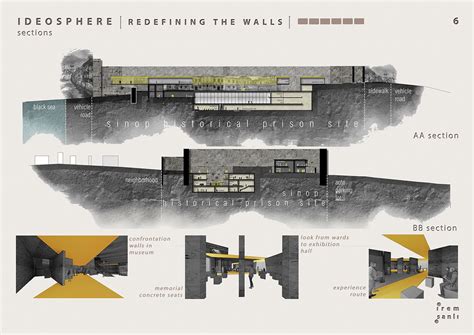
Architectural presentation boards
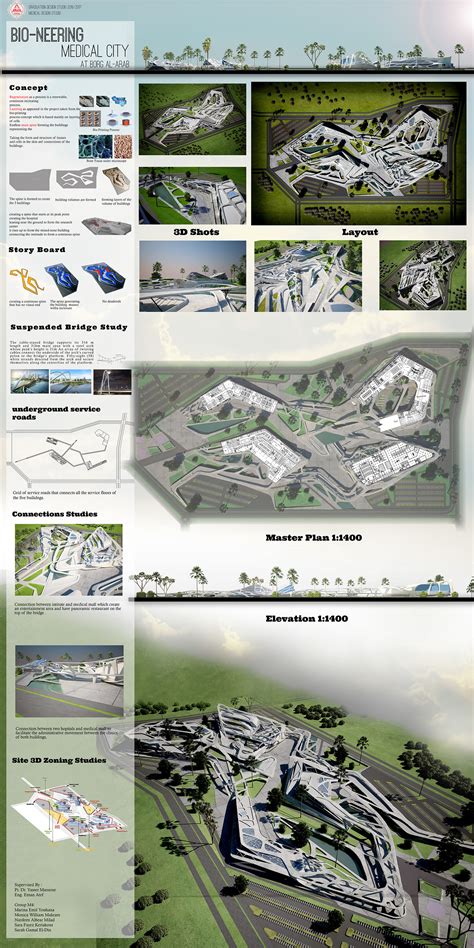
Graphic design in architecture, particularly focusing on architectural presentation boards, demands a meticulous and strategic approach to visually communicating complex architectural ideas effectively. These boards serve not merely as a medium for exhibiting technical drawings but also as a canvas where aesthetic appeal and informative content merge seamlessly to narrate the architectural story. Each element, from the choice of typography to the arrangement of images and diagrams, must adhere to a coherent visual hierarchy that guides the viewer's eye strategically, ensuring critical information is easily digestible. By employing techniques such as color theory, proportion, and negative space, a designer can create a balanced layout that not only enhances the visual impact of the board but also reinforces the conceptual clarity of the architectural proposal presented.




















Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.