Graphic design for film emerged as a pivotal craft during the golden age of cinema, when filmmakers needed to visually communicate their stories with flair and originality. Initially, there was a standard approach to design, but today, graphic design for film includes a rich tapestry of innovative ideas. Whether through title sequences, posters, or props, this form of design enhances storytelling and adds depth to the cinematic experience. While some might assume this niche field is all technical precision and rigidity, it is, in fact, a canvas for boundless creativity and thematic exploration--and it's more crucial than ever in the film industry. Elevate your film projects with these inspiring graphic design strategies and create unforgettable visual narratives of your own.
Key art design
Key art design in film serves as the primary visual representation of a movie's narrative and tone, encapsulating the essence of the film in a single compelling image. Graphic designers in this realm meticulously craft compositions that balance elements like typography, color palette, and iconic imagery to evoke emotions and generate curiosity among potential audiences. The process involves close collaboration with filmmakers and marketers to ensure cohesive branding across all promotional materials, making the design not only a visually arresting piece but also a strategic marketing tool. an effective key art design must communicate the film's genre, plot intrigue, and unique selling proposition within mere seconds, convincing viewers to explore further depth within the cinematic experience.
Title sequence design
Title sequence design in film involves a multifaceted process that combines creativity and technical skill to convey the film's essence, thematic elements, and stylistic tone. Designers meticulously analyze the script and thematic undertone, selecting typography, color palettes, and motion graphics that evoke the intended mood, whether it be suspenseful, whimsical, or dramatic. Each sequence often serves as a narrative device, foreshadowing plot elements or introducing key characters and settings through subtle visual cues and meticulously crafted transitions. Designers employ innovative techniques such as kinetic typography, animations, and custom illustrations, leveraging software tools like After Effects and Cinema 4D to seamlessly integrate these elements with the score, ensuring that the aesthetics align cohesively with the director's vision and the film's overarching narrative structure.
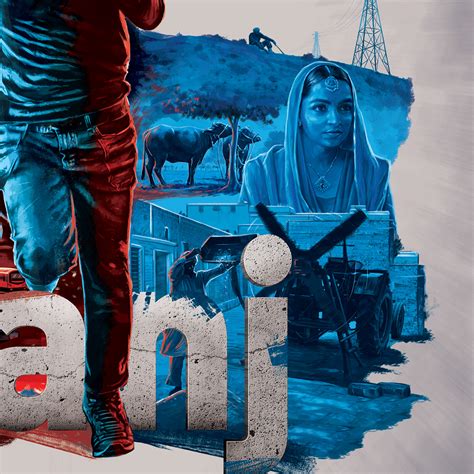
Movie poster layout
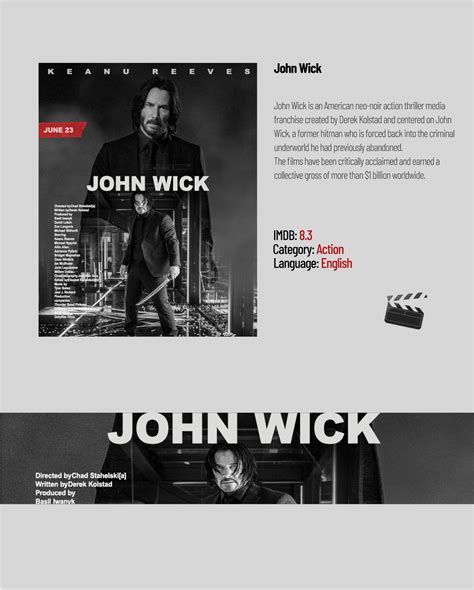
Graphic design for film, particularly in the realm of movie poster layout, involves a careful orchestration of visual elements to both capture the essence of the film and entice the audience. The layout starts with a hierarchy of images and text; the focal point typically being the striking visual or photograph that represents the film's unique selling point, often featuring a leading character or a climactic scene. Surrounding this central image, elements such as the film's title employ bold typography to catch the viewer's attention from afar, usually integrated with stylistic elements that hint at the film's genre--be it the gritty textures for a thriller or the vibrant palettes for a romantic comedy. The eye is guided through the composition with the strategic placement of the tagline, key credits, and logos, balancing artistic creativity with clarity, ensuring that all textual information is legible yet seamlessly woven into the overall aesthetic narrative that leaves a lingering curiosity with potential viewers.
Film branding aesthetics
Film branding aesthetics in graphic design encapsulate a nuanced symbiosis between visual artistry and narrative evocation, demanding an acute awareness of color theory, typographic expression, and compositional balance to convey the film's essence. This intricate process involves crafting distinctive visual identities through meticulously designed posters, title sequences, and promotional materials that collectively encapsulate and communicate the film's thematic undertones and emotional journey. Graphic designers adept in this niche tap into the psychological impact of imagery and symbolism, employing strategies like palette selection that mirrors the film's mood or cultural setting, and using typography that resonates with the period or genre depicted, all to achieve a cohesive brand perception. The success of these visual components hinges on their ability to subliminally prime audience expectations and engender emotional connections even before they experience the actual motion picture, thus underscoring the pivotal role of graphic design in the cinematic sphere.
Typography selection
Typography in film graphic design requires a nuanced understanding of the story's tone, period, and intended emotional impact. A sans-serif font might be chosen for a modern sci-fi film, embodying sleekness and futurism, while a serif font could ground a historical drama with its classic, traditional aesthetic. The color, placement, and size of the type are meticulously considered to ensure legibility and to capture the viewer's attention without detracting from the visuals. In sophisticated sequences, kinetic typography adds dynamism, allowing words to animate in sync with the soundtrack, enhancing the narrative's flow and maintaining viewer immersion.
Color palette creation
Graphic design for film involves the meticulous selection and creation of color palettes that serve as visual narratives, profoundly affecting the viewer's emotional experience and the film's overarching tone. Each color choice is deliberate, taking into consideration the psychological associations and cultural connotations to subtly influence the audience's perception and interpretation of the storyline. For instance, warm colors like reds and oranges may be used to evoke feelings of passion or danger, while cooler tones like greens and blues can create a sense of calmness or melancholy, aligning with the film's thematic nuances. The graphic designer collaborates closely with filmmakers to ensure this chromatic coherence, harmonizing with lighting, costume, and set design, thus crafting a visually compelling world that resonates with the cinematic vision.
Concept development sketches
In graphic design for film, concept development sketches serve as the foundational visual exploration phase, where artists meticulously brainstorm and translate narrative ideas into captivating imagery that supports the director's vision. Skilled designers employ an array of techniques such as freehand drawing, digital sketching, and mixed media to experiment with mood, composition, and style. These sketches frequently involve multiple iterations to refine aspects like character design, environment settings, and iconic props essential to the storyline, all while maintaining harmony with the film's thematic elements. Artists communicate these initial ideas to the production team, enabling a cohesive visual language that guides further design processes, ensuring the final film reflects a unified aesthetic congruent with its narrative essence.
Visual storytelling elements
Graphic design in film serves as a crucial storytelling tool, seamlessly integrating visual storytelling elements to enhance the narrative. Color palettes are meticulously curated to evoke certain emotions, establishing mood and tone that align with character arcs and plot progression. Typography for credits and title sequences becomes a narrative mechanism, reflecting the theme and era or setting, thereby grounding the audience in the film's universe. Shapes, lines, and symmetry are strategically employed in scene composition, drawing the viewer's eye to focal points, shaping perception, and leading to an immersive cinematic experience that supports and amplifies the director's vision.
Composition and framing
Graphic design for film relies heavily on composition and framing to convey narratives and emotions effectively. Composition involves the deliberate arrangement of visual elements within a frame, ensuring balance and harmony while guiding the viewer's eye to specific focal points. Framing, the act of determining what is seen on screen, further emphasizes the importance of how subjects and background interact within the cinematic space, using techniques like the rule of thirds or leading lines to enhance storytelling. Designers also manipulate color, contrast, and spatial relationships within each frame to create mood, suggest themes, and support the director's vision, ultimately crafting a visual language that resonates with audiences on an intellectual and emotional level.
Interactive digital displays
Interactive digital displays in film not only serve as a mesmerizing visual element but also function as a narrative device, enriching the viewer's experience by offering a dynamic blend of story and spectacle. Filmmakers, leveraging sophisticated software, create these displays with meticulous attention to detail, crafting interfaces that feel authentic and enhance world-building. These displays often feature in genres such as sci-fi or thriller, where audiences expect cutting-edge technology that mirrors or even surpasses real-world advancements. Designers must consider how these screens interact with actors, plot progression, and the overall mise-en-scene, ensuring that each holographic projection or virtual interface seamlessly integrates into the film's aesthetic while advancing the storyline and immersing the audience deeper into the cinematic universe.














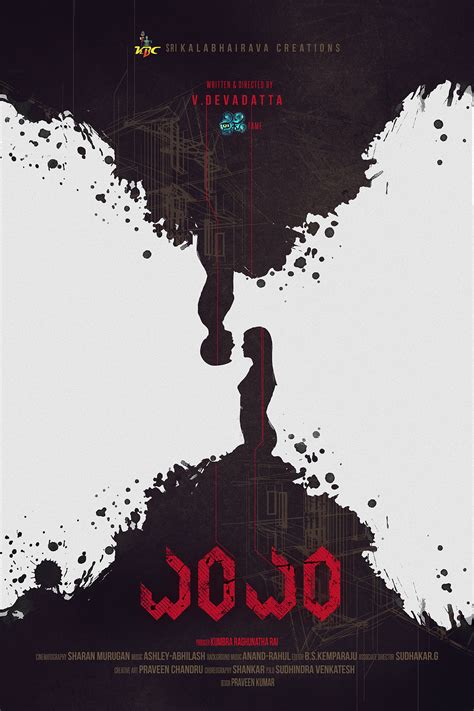













Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.